Resources
Partner websites
Software
Human Cell Map
The Human Cell Map is a project to map the cell using the biotin-based proximity-labelling technique BioID. It currently contains localization information on over 4000 proteins in HEK 293 cells.
![Screenshot of GIX report on PubMed]()
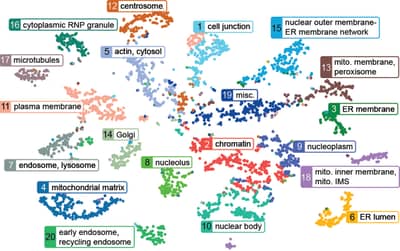
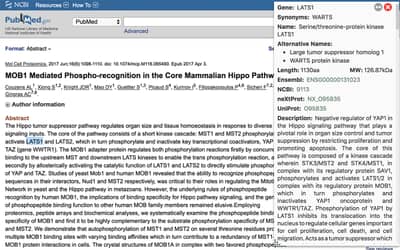
Gene Information eXtension (GIX)
Gene Information eXtension (GIX) is a browser extension for Chrome, Edge, Firefox and Safari that allows users to retrieve gene information directly on any website simply by double clicking a gene name. It supports several organisms and gene reports are customizable.
![Screenshot of GIX report on PubMed]()
ProHits-viz
James Knight developed interactive analysis visualization tools for interaction proteomics that enable organizing bait-prey data as heat maps or dot plots, quantitatively comparing two baits, calculating the specificity of preys across baits jointly analyzed, and analyzing the prey-prey relationships (a feature that is most useful for proximity biotinylation studies). With a simple text-based input compatible with SAINT or CRAPome outputs, this web-based resource should facilitate interaction proteomics analysis and visualization.
![Screenshot of ProHits-viz home page]()
ProHits 8.0: Ready for DIA analysis
Guomin (Frank) Liu and colleagues in the Gingras, Nesvizhskii, Bandeira, Choi, Tyers and Raught labs release a major update to the ProHits LIMS. In ProHits 8.0, Data Independent Acquisition (DIA) is handled through DIA-Umpire, MSPLIT-DIA, mapDIA and SAINT-intensity. ProHits 8.0 also facilitates data deposition in public repositories such as MassIVE and the transfer of data to new visualization tools we have developed.
DIA-Umpire: Integrated solution for Data Independent Acquisition
![DIA-Umpire logo]()
Chih-Chiang Tsou from the Nesvizhskii lab developed, in collaboration with the Gingras lab, DIA-Umpire, an integrated platform for untargeted and semi-targeted identification and quantification from Data Independent Acquisition. DIA-Umpire works on the basis of demultiplexing complex spectra through retention time alignment of MS1 and MS2 peaks and generation of pseudo-MS/MS spectra that can be searched using standard tools developed for shotgun proteomics. DIA-Umpire is integrated in the next public release of ProHits, in addition to being available as a stand-alone tool.
MSPLIT-DIA: spectral matching tool for Data Independent Acquisition
Jian Wang from the Bandeira lab developed, in collaboration with the Gingras lab, MSPLIT-DIA, a spectral library matching tool for Data Independent Analysis. MSPLIT-DIA demultiplexes complex spectra through spectral projection, leading to the sensitive identification of peptides in DIA data. Used as a stand-alone, MSPLIT-DIA performs sensitive spectral counting compatible with SAINT analysis, and can also generate assay-specific libraries for targeted re-extraction.
SAINT series of software tools
Significance Analysis of INTeractome (SAINT) tools for interaction scoring were initially developed for unsupervised analysis of interactome data (Science, 2010), but rapidly adapted by Hyungwon Choi (Nat Methods, 2011), for semi-supervised analysis of spectral-count based interaction proteomics data using negative controls. More recent advances include the extension to intensity data (JPR, 2012), the implementation of the computationally efficient SAINTexpress (J Proteomics, 2015) and in 2016, the extension of the SAINT-intensity framework to peptides and transitions, for adaptation to Data Independent Analysis (DIA) data (Proteomics, 2016).
- SAINT is maintained by Hyungwon Choi.
- SAINT scoring is implemented within the ProHits LIMS, in the Contaminant Repository for Affinity Purification (CRAPome) and for use with our visualization tools (ProHits-viz).
ProHits-web: web-accessible quantitative interaction repository
Interaction proteomics repository for the Gingras lab and our collaborators. The repository is meant to support publications by offering access to high quality quantitative interaction proteomics data and other supplementary material through easy graphical user interfaces. We also use the resource to give password-protected access to specific datasets to collaborators and/or reviewers. Developed by JianPian Zhang and Guomin (Frank) Liu.
- ProHits-web
- Publication
- Major datasets currently in ProHits-web include: the HSP90 co-chaperone specificity dataset (Taipale et al., Cell, 2014), an interaction dataset for the myotubularin phosphatases (St-Denis et al., Mol Cell Proteomics, 2015) and a comprehensive map of the centrosome-cilium interface (Gupta et al., Cell, 2015).
CRAPome: Contaminant Repository for Affinity Purification
Database of annotated negative controls contributed by the research community to help distinguish real interactions from the non-specific background.
- CRAPome, designed by Datta Mellacheruvu and Zach Wright (Nesvizhskii lab).
- Publication
ProHits - interaction proteomics LIMS
This software helps manage interaction proteomics data. Developed by Guomin (Frank) Liu and JianPian Zhang.
SAINT version 1 - unsupervised model
SAINT version 1.0 allows users to define interaction significance based on label-free quantitative AP-MS data (optimized for large-scale datasets with no control runs).
Nested clusters
This software helps in the identification of protein complexes from AP-MS data.
- Nested cluster, developed by Hyungwon Choi.
- Publication
Protocols
Affinity-purification coupled to mass spectrometry in human cells
Protocols
Sources: Gingras et al., Mol Cell Proteomics, 2005; Chen and Gingras, Methods, 2007; Chen et al., J Biol Chem, 2008; Goudreault et al., Mol Cell Proteomics, 2009
Mammlian FLAG AP-MS Protocols
Protocols
- Anti-FLAG AP-MS with Magnetic beads 2012
- Anti-FLAG AP-MS with Agarose beads 2012
- 293 Flp-In FLAG magnetic AP - July 2013
Source: Kean et al., Methods, 2012
Affinity-purification coupled to mass spectrometry in S. cerevisiae
Protocols
293 Flp-In FLAG magnetic chromatin optimized AP protocol
Protocol
Flp-In BioID Streptavidin sepharose chromatin optizided
Protocol
Flp-In BioID Streptavidin sepharose protocol
Protocol
Source: Couzens et al., Sci Signal, 2013
Reagents
Cloning vector - pcDNA5-FRT-FLAG & pcDNA5-FRT-eGFP
Sequence of the cloning vector pcDNA5-FRT-FLAG and pcDNA5-FRT-eGFP, for N-terminal tagging and expression in the Invitrogen Flp-In T-REx system.
Sequence
Map
Source: Kean et al., J Biol Chem, 2011
Cloning Vectors: pDEST-pcDNA5-FLAG N-term & pDEST-pcDNA5-FLAG C-term
Gateway compatible vectors for N-terminal or C-terminal tagging and expression in the Invitrogen Flp-In T-REx system.
Sequence
Map
Source: Couzens et al., Sci Signal, 2013
BioID Cloning Vectors: pDEST-pcDNA5-BirA-FLAG N-term & pDEST-pcDNA5-BirA-FLAG C-term
Gateway compatible vectors for N-terminal or C-terminal tagging and expression in the Invitrogen Flp-In T-REx system for BioID.
Sequence
Map
Source: Couzens et al., Sci Signal, 2013
BioID control vectors: pDEST-pcDNA5-BirA-FLAG-GFP and pDEST-pcDNA5-FLAG-NLS-BirA
Vector controls for use with Invitrogen’s Flp-In T-REx system for BioID. Please refer to Couzens et al., 2013 in any publication using the BirA-FLAG-GFP vector and to Lambert et al, 2015 for the FLAG-NLS-BirA vector.
Sequence
Sources: Couzens et al., Sci Signal, 2013; Lambert et al., J Proteomics, 2015
Data
Interaction data now at ProHits-web
Since 2013, our datasets are released through ProHits-web. We also deposit curated interaction lists at IntAct and BioGRID and our mass spectrometry data at MassIVE.
Breitkreutz et al., Science, 2010
&ldqio;A global protein kinase and phosphatase interaction network in yeast&rdqio;. High-confidence interactions were deposited in the BioGrid and IntAct databases.
- YeastKinome.org, developed by C Stark and BJ Breitkreutz.
Goudreault et al., Mol Cell Proteomics, 2009
All reported interactions were deposited in the BioGrid and IntAct interaction databases.
Chen et al., J Biol Chem, 2008
All reported interactions were deposited in the BioGrid and IntAct interaction databases.